YOU HAVE CHOSEN THE ELEMENT:

BISMUTH
Bismuth, the 83rd element on the periodic table, is quite unique. Although it was discovered in ancient times, Bismuth was often times confused with lead, tin and zinc until the 18th century. Bismuth is a typical metal by comparison. But it also has some unique properties to it.
With an atomic weight of 208.98 grams and a melting point and boiling point of 271 degrees Celsius and 1560 degrees Celsius, respectively, Bismuth is one of the largest non-radioactive elements. It is found in the Earth's crust at medium intervals, and is usually in the form of Nitrates, some of which decompose into simple forms after a short time.
Uses for Bismuth vary. It can be used as a medicine, cosmetic, castings, alloys, magnetic field and electrical field measuring devices, and in fluoroscopy. Bismuth's poor conduction of electricity and heat and its ability to create low boiling point alloys are used to create castings or molds.
Bismuth's special properties make it one of the most unique of the metals. It allows Bismuth to be used for a variety of different reasons. The compounds formed with Bismuth are used by many people unknowingly. Bismuth is a great element and its compound's range from Make-up to medicine to alloys. Without Bismuth, the world would be a different place.
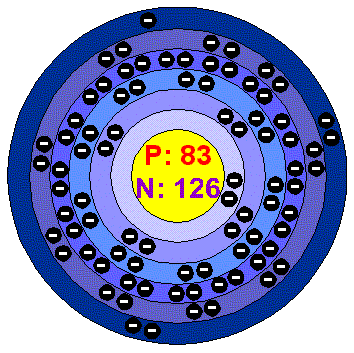
BELOW IS A PICTURE OF BISMUTH AND IT'S ELECTRON CONFIGURATION