YOU HAVE CHOSEN THE ELEMENT:

NITROGEN
Founded in 1772 by a British physician Daniel Rutherford, Nitrogen was not recognized as an elemental gas until 1776, when French chemist Antione Laurent Lavoisier conducted studies into its origin and thus proposed the idea that Nitrogen was found in the Earth's atmosphere as a natural element.
Nitrogen, a non-toxic, odorless, tasteless, colorless gas makes up the 7th spot on the periodic table. This common gas can be found in fertilizer, ammonia, and even our atmosphere. Nitrogen alone makes up about 78% of our natural atmosphere.
Nitrogen is a di-atomic element and has an atomic weight of 14.007 grams.
Temperatures of -210.01 degrees Celsius (that's -346.02 degrees Fahrenheit) are required to melt this non-metal, while a temperature of -195.79 degrees C (-320.42 degrees F) is necessary to boil Nitrogen.
Nitrogen can be obtained from the atmosphere by passing air over heated Copper and/or Iron. The oxygen is removed, leaving only the Nitrogen (and inert gasses) to be collected. Pure Nitrogen can only be obtained by fractional distillation of liquid air, being that liquid nitrogen has a lower boiling point than liquid oxygen, thus filtering out first.
Nitrogen is required by Oxygen to aid in burning and respiration processes. It also is an essential part of plant life. Several bacteria found in the soil convert atmospheric Nitrogen into a different form, like a nitrate. This new type of Nitrogen can be absorbed by plants in a process called Nitrogen Fixation. Nitrogen can also take the form of a protein, aiding animal tissues.
Nitrogen, generally, is not very reactive, and only combines with other elements at high temperatures or pressures. As an active form, Nitrogen must first pass through an electric charge at low pressures. This allows nitrogen to react with certain elements to produce azides, nitrides, and Hydrocyanic acid and/or cyanides.
This may not mean much, but Nitrogen plays an important part in every day life. Nitrogen is used to produce ammonia, which in turn becomes an ingredient in several commonly used compounds. A few of these include fertilizer, laughing gas, anesthetic, cryogenics, and as a coolant when reacting with certain ceramic materials.
So the next time you plant some flowers, go in for some much-needed surgery, or simply take a breath of air remember, your using Nitrogen.
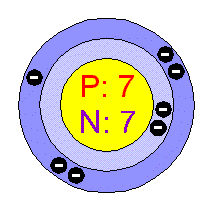
BELOW IS A PICTURE OF NITROGEN AND ITS ELECTRON CONFIGURATION